Export search results as:
BibTex
2006
Tracking complex objects using graphical object models
Sigal, L., Zhu, Y., Comaniciu, D. and
Black, M.J.
In
International Workshop on Complex Motion,
Springer-Verlag,
Vol. LNCS 3417,
pages 223-234,
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

Efficient belief propagation with learned higher-order Markov random fields
Lan, X., Roth, S., Huttenlocher, D. and
Black, M.J.
In
European Conference on Computer Vision, ECCV,
Vol. II,
pages 269-282,
Graz, Austria.
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

Measure locally, reason globally: Occlusion-sensitive articulated pose estimation
Sigal, L. and
Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR,
Vol. 2,
pages 2041-2048,
New York, NY.
June
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

An adaptive appearance model approach for model-based articulated object tracking
Balan, A. and
Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR,
Vol. 1,
pages 758-765,
New York, NY.
June
2006.
Abstract:
▸
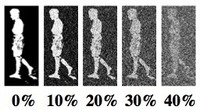
The detection and tracking of three-dimensional human body models has progressed rapidly but successful approaches typically rely on accurate foreground silhouettes obtained using background segmentation. There are many practical applications where such information is imprecise. Here we develop a new image likelihood function based on the visual appearance of the subject being tracked. We propose a robust, adaptive, appearance model based on the Wandering-Stable-Lost framework extended to the case of articulated body parts. The method models appearance using a mixture model that includes an adaptive template, frame-to-frame matching and an outlier process. We employ an annealed particle filtering algorithm for inference and take advantage of the 3D body model to predict self occlusion and improve pose estimation accuracy. Quantitative tracking results are presented for a walking sequence with a 180 degree turn, captured with four synchronized and calibrated cameras and containing significant appearance changes and self-occlusion in each view.
[Share]
Sending email...

Specular flow and the recovery of surface structure
In
Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR,
Vol. 2,
pages 1869-1876,
New York, NY.
June
2006.
Abstract:
▸
In scenes containing specular objects, the image motion observed by a moving camera may be an intermixed combination of optical flow resulting from diffuse reflectance (diffuse flow) and specular reflection (specular flow). Here, with few assumptions, we formalize the notion of specular flow, show how it relates to the 3D structure of the world, and develop an algorithm for estimating scene structure from 2D image motion. Unlike previous work on isolated specular highlights we use two image frames and estimate the semi-dense flow arising from the specular reflections of textured scenes. We parametrically model the image motion of a quadratic surface patch viewed from a moving camera. The flow is modeled as a probabilistic mixture of diffuse and specular components and the 3D shape is recovered using an Expectation-Maximization algorithm. Rather than treating specular reflections as noise to be removed or ignored, we show that the specular flow provides additional constraints on scene geometry that improve estimation of 3D structure when compared with reconstruction from diffuse flow alone. We demonstrate this for a set of synthetic and real sequences of mixed specular-diffuse objects.
[Share]
Sending email...

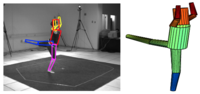
Predicting 3D people from 2D pictures
(Best Paper)
Sigal, L. and
Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IV Conf. on Articulated Motion and DeformableObjects (AMDO),
Vol. LNCS 4069,
pages 185-195,
July
2006.
Abstract:
▸
We propose a hierarchical process for inferring the 3D pose of a person from monocular images. First we infer a learned view-based 2D body model from a single image using non-parametric belief propagation. This approach integrates information from bottom-up body-part proposal processes and deals with self-occlusion to compute distributions over limb poses. Then, we exploit a learned Mixture of Experts model to infer a distribution of 3D poses conditioned on 2D poses. This approach is more general than recent work on inferring 3D pose directly from silhouettes since the 2D body model provides a richer representation that includes the 2D joint angles and the poses of limbs that may be unobserved in the silhouette. We demonstrate the method in a laboratory setting where we evaluate the accuracy of the 3D poses against ground truth data. We also estimate 3D body pose in a monocular image sequence. The resulting 3D estimates are sufficiently accurate to serve as proposals for the Bayesian inference of 3D human motion over time
[Share]
Sending email...

Denoising archival films using a learned Bayesian model
Moldovan, T.M., Roth, S. and
Black, M.J.
In
Int. Conf. on Image Processing, ICIP,
pages 2641-2644,
Atlanta.
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

Statistical analysis of the non-stationarity of neural population codes
Kim, S.-P., Wood, F., Fellows, M., Donoghue, J.P. and
Black, M.J.
In
BioRob 2006, The first IEEE / RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics,
pages 295-299,
Pisa, Italy.
February
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

A non-parametric Bayesian approach to spike sorting
Wood, F., Goldwater, S. and
Black, M.J.
In
International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS,
pages 1165-1169,
New York, NY.
August
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

Nonlinear physically-based models for decoding motor-cortical population activity
Shakhnarovich, G., Kim, S.-P. and
Black, M.J.
In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19, NIPS-2006,
MIT Press,
pages 1257-1264,
2006.
[Share]
Sending email...

2005
On the receptive fields of Markov random fields: Predictions from a probabilistic model of scene statistics
Black, M.J. and Roth, S.
COSYNE 2005,
Salt Lake City.
March
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

Energy-based models of motor cortical population activity
Wood, F. and Black, M.
Program No. 689.20. 2005 Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner,
Society for Neuroscience,
Washington, DC.
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

Motor cortical decoding using an autoregressive moving average model
Fisher, J. and
Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,
pages 1469-1472,
September
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

Inferring attentional state and kinematics from motor cortical firing rates
Wood, F., Prabhat, Donoghue, J.P. and
Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,
pages 1544-1547,
September
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

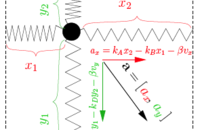
Modeling neural population spiking activity with Gibbs distributions
Wood, F., Roth, S. and
Black, M.J.
In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18,
pages 1537-1544,
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

Visual motion analysis method for detecting arbitrary numbers of moving objects in image sequences
Jepson, A.D., Fleet, D.J. and
Black, M.J.
US Pat. 6,954,544,
October
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

Fields of Experts: A framework for learning image priors
In
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
Vol. 2,
pages 860-867,
June
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

A quantitative evaluation of video-based 3D person tracking
Balan, A.O., Sigal, L. and
Black, M.J.
The Second Joint IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, VS-PETS,
pages 349-356,
October
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

On the spatial statistics of optical flow
(Marr Prize, Honorable Mention)
In
International Conf. on Computer Vision,
pages 42-49,
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

Representing cyclic human motion using functional analysis
Ormoneit, D.,
Black, M.J., Hastie, T. and Kjellström, H.
Image and Vision Computing,
23(14):1264-1276,
December
2005.
Abstract:
▸
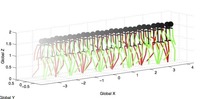
We present a robust automatic method for modeling cyclic 3D human motion such as walking using motion-capture data. The pose of the body is represented by a time-series of joint angles which are automatically segmented into a sequence of motion cycles. The mean and the principal components of these cycles are computed using a new algorithm that enforces smooth transitions between the cycles by operating in the Fourier domain. Key to this method is its ability to automatically deal with noise and missing data. A learned walking model is then exploited for Bayesian tracking of 3D human motion.
[Share]
Sending email...

A Flow-Based Approach to Vehicle Detection and Background Mosaicking in Airborne Video
Yalcin, H., Collins, R.,
Black, M. and Hebert, M.
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Video Proceedings,,
2005.
[Share]
Sending email...

2004
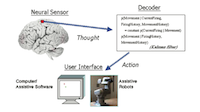
A direct brain-machine interface for 2D cursor control using a Kalman filter
Shaikhouni, A., Wu, W., Moris, D.S., Donoghue, J.P. and Black, M.J.
Society for Neuroscience,
2004.
Online.
[Share]
Sending email...

Development of neural motor prostheses for humans
Donoghue, J., Nurmikko, A., Friehs, G. and
Black, M.
In
Advances in Clinical Neurophysiology,
Hallett, M., Phillips, L.H., Schomer, D.L. and Massey, J.M., Editors,
Supplements to Clinical Neurophysiology Vol. 57,
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

Automatic spike sorting for neural decoding
Wood, F.D., Fellows, M., Donoghue, J.P. and Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,
pages 4009-4012,
September
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

Closed-loop neural control of cursor motion using a Kalman filter
Wu, W., Shaikhouni, A., Donoghue, J.P. and
Black, M.J.
In
Proc. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,
pages 4126-4129,
September
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

3D human limb detection using space carving and multi-view eigen models
Bhatia, S., Sigal, L., Isard, M. and
Black, M.J.
In
IEEE Workshop on Articulated and Nonrigid Motion,
June
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

The dense estimation of motion and appearance in layers
Yalcin, H.,
Black, M.J. and Fablet, R.
In
IEEE Workshop on Image and Video Registration,
June
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

Gibbs likelihoods for Bayesian tracking
Roth, S., Sigal, L. and
Black, M.J.
In
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
Vol. 1,
pages 886-893,
June
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

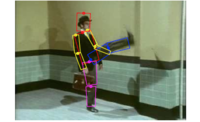
Tracking loose-limbed people
Sigal, L., Bhatia, S., Roth, S.,
Black, M.J. and Isard, M.
In
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
Vol. 1,
pages 421-428,
June
2004.
[Share]
Sending email...

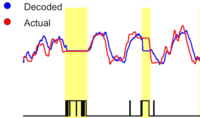
Modeling and decoding motor cortical activity using a switching Kalman filter
Wu, W.,
Black, M.J., Mumford, D., Gao, Y., Bienenstock, E. and Donoghue, J.P.
IEEE Trans. Biomedical Engineering,
51(6):933-942,
June
2004.
Abstract:
▸
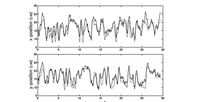
We present a switching Kalman filter model for the real-time inference of hand kinematics from a population of motor cortical neurons. Firing rates are modeled as a Gaussian mixture where the mean of each Gaussian component is a linear function of hand kinematics. A “hidden state” models the probability of each mixture component and evolves over time in a Markov chain. The model generalizes previous encoding and decoding methods, addresses
the non-Gaussian nature of firing rates, and can cope with crudely sorted neural data common in on-line prosthetic applications.
[Share]
Sending email...

2003
Specular flow and the perception of surface reflectance
Roth, S., Domini, F. and Black, M.J.
Journal of Vision, 3 (9): 413a,
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

A Gaussian mixture model for the motor cortical coding of hand motion
Wu, W., Mumford, D., Black, M.J., Gao, Y., Bienenstock, E. and Donoghue, J.P.
Neural Control of Movement,
Santa Barbara, CA.
April
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

Neural decoding of cursor motion using a Kalman filter
(Nominated: Best student paper)
Wu, W.,
Black, M.J., Gao, Y., Bienenstock, E., Serruya, M., Shaikhouni, A. and Donoghue, J.P.
In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 15,
MIT Press,
pages 133-140,
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

A quantitative comparison of linear and non-linear models of motor cortical activity for the encoding and decoding of arm motions
Gao, Y.,
Black, M.J., Bienenstock, E., Wu, W. and Donoghue, J.P.
In
1st International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering,
pages 189-192,
Capri, Italy.
March
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

Connecting brains with machines: The neural control of 2D cursor movement
Black, M.J., Bienenstock, E., Donoghue, J.P., Serruya, M., Wu, W. and Gao, Y.
In
1st International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering,
pages 580-583,
Capri, Italy.
March
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

A switching Kalman filter model for the motor cortical coding of hand motion
Wu, W.,
Black, M.J., Mumford, D., Gao, Y., Bienenstock, E. and Donoghue, J.P.
In
Proc. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,
pages 2083-2086,
September
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...


Attractive people: Assembling loose-limbed models using non-parametric belief propagation
Sigal, L., Isard, M.I., Sigelman, B.H. and
Black, M.J.
In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16, NIPS,
MIT Press,
pages 1539-1546,
2003.
Abstract:
▸
The detection and pose estimation of people in images and video is made challenging by the variability of human appearance, the complexity of natural scenes, and the high dimensionality of articulated body models. To cope with these problems we represent the 3D human body as a graphical model in which the relationships between the body parts are represented by conditional probability distributions. We formulate the pose estimation problem as one of probabilistic inference over a graphical model where the random variables correspond to the individual limb parameters (position and orientation). Because the limbs are described by 6-dimensional vectors encoding pose in 3-space, discretization is impractical and the random variables in our model must be continuous-valued. To approximate belief propagation in such a graph we exploit a recently introduced generalization of the particle filter. This framework facilitates the automatic initialization of the body-model from low level cues and is robust to occlusion of body parts and scene clutter.
[Share]
Sending email...


Learning the statistics of people in images and video
Sidenbladh, H. and
Black, M.J.
International Journal of Computer Vision,
54(1-3):183-209,
August
2003.
Abstract:
▸
This paper address the problems of modeling the appearance of humans and distinguishing human appearance from the appearance of general scenes. We seek a model of appearance and motion that is generic in that it accounts for the ways in which people's appearance varies and, at the same time, is specific enough to be useful for tracking people in natural scenes. Given a 3D model of the person projected into an image we model the likelihood of observing various image cues conditioned on the predicted locations and orientations of the limbs. These cues are taken to be steered filter responses corresponding to edges, ridges, and motion-compensated temporal differences. Motivated by work on the statistics of natural scenes, the statistics of these filter responses for human limbs are learned from training images containing hand-labeled limb regions. Similarly, the statistics of the filter responses in general scenes are learned to define a “background” distribution. The likelihood of observing a scene given a predicted pose of a person is computed, for each limb, using the likelihood ratio between the learned foreground (person) and background distributions. Adopting a Bayesian formulation allows cues to be combined in a principled way. Furthermore, the use of learned distributions obviates the need for hand-tuned image noise models and thresholds. The paper provides a detailed analysis of the statistics of how people appear in scenes and provides a connection between work on natural image statistics and the Bayesian tracking of people.
[Share]
Sending email...

Guest editorial: Computational vision at Brown
Black, M.J. and Kimia, B.
International Journal of Computer Vision,
54(1-3):5-11,
August
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

Apparatus and method for identifying and tracking objects with view-based representations
Black, M.J. and Jepson, A.D.
US Pat. 6,526,156,
February
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

Method and apparatus for generating a condensed version of a video sequence including desired affordances
Black, M.J., Ju, S., Minneman, S. and Kimber, D.
US Pat. 6,560,281,
May
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...

Image statistics and anisotropic diffusion
Scharr, H.,
Black, M.J. and Haussecker, H.
In
Int. Conf. on Computer Vision,
pages 840-847,
October
2003.
[Share]
Sending email...


A framework for robust subspace learning
De la Torre, F. and
Black, M.J.
International Journal of Computer Vision,
54(1-3):117-142,
August
2003.
Abstract:
▸
Many computer vision, signal processing and statistical problems can be posed as problems of learning low dimensional linear or multi-linear models. These models have been widely used for the representation of shape, appearance, motion, etc., in computer vision applications. Methods for learning linear models can be seen as a special case of subspace fitting. One draw-back of previous learning methods is that they are based on least squares estimation techniques and hence fail to account for “outliers” which are common in realistic training sets. We review previous approaches for making linear learning methods robust to outliers and present a new method that uses an intra-sample outlier process to account for pixel outliers. We develop the theory of Robust Subspace Learning (RSL) for linear models within a continuous optimization framework based on robust M-estimation. The framework applies to a variety of linear learning problems in computer vision including eigen-analysis and structure from motion. Several synthetic and natural examples are used to develop and illustrate the theory and applications of robust subspace learning in computer vision.
[Share]
Sending email...

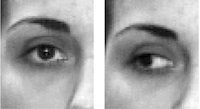
Robust parameterized component analysis: Theory and applications to 2D facial appearance models
De la Torre, F. and
Black, M.J.
Computer Vision and Image Understanding,
91(1-2):53-71,
July
2003.
Abstract:
▸
Principal component analysis (PCA) has been successfully applied to construct linear models of shape, graylevel, and motion in images. In particular, PCA has been widely used to model the variation in the appearance of people's faces. We extend previous work on facial modeling for tracking faces in video sequences as they undergo significant changes due to facial expressions. Here we consider person-specific facial appearance models (PSFAM), which use modular PCA to model complex intra-person appearance changes. Such models require aligned visual training data; in previous work, this has involved a time consuming and error-prone hand alignment and cropping process. Instead, the main contribution of this paper is to introduce parameterized component analysis to learn a subspace that is invariant to affine (or higher order) geometric transformations. The automatic learning of a PSFAM given a training image sequence is posed as a continuous optimization problem and is solved with a mixture of stochastic and deterministic techniques achieving sub-pixel accuracy. We illustrate the use of the 2D PSFAM model with preliminary experiments relevant to applications including video-conferencing and avatar animation.
[Share]
Sending email...

2002
Inferring hand motion from multi-cell recordings in motor cortex using a Kalman filter
Wu, W., M., B., Gao, Y., Bienenstock, E., Serruya, M. and Donoghue, J.
Program No. 357.5. 2002 Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner,
Society for Neuroscience,
Washington, DC.
2002.
Online.
[Share]
Sending email...


Bayesian Inference of Visual Motion Boundaries
Fleet, D.J.,
Black, M.J. and Nestares, O.
In
Exploring Artificial Intelligence in the New Millennium,
Lakemeyer, G. and Nebel, B., Editors,
pages 139-174,
Morgan Kaufmann Pub.,
July
2002.
Abstract:
▸
This chapter addresses an open problem in visual motion analysis, the estimation of image motion in the vicinity of occlusion boundaries. With a Bayesian formulation, local image motion is explained in terms of multiple, competing, nonlinear models, including models for smooth (translational) motion and for motion boundaries. The generative model for motion boundaries explicitly encodes the orientation of the boundary, the velocities on either side, the motion of the occluding edge over time, and the appearance/disappearance of pixels at the boundary. We formulate the posterior probability distribution over the models and model parameters, conditioned on the image sequence. Approximate inference is achieved with a combination of tools: A Bayesian filter provides for online computation; factored sampling allows us to represent multimodal non-Gaussian distributions and to propagate beliefs with nonlinear dynamics from one time to the next; and mixture models are used to simplify the computation of joint prediction distributions in the Bayesian filter. To efficiently represent such a high-dimensional space, we also initialize samples using the responses of a low-level motion-discontinuity detector. The basic formulation and computational model provide a general probabilistic framework for motion estimation with multiple, nonlinear models.
[Share]
Sending email...

Probabilistic inference of hand motion from neural activity in motor cortex
Gao, Y.,
Black, M.J., Bienenstock, E., Shoham, S. and Donoghue, J.
In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 14,
MIT Press,
pages 221-228,
2002.
[Share]
Sending email...

Inferring hand motion from multi-cell recordings in motor cortex using a Kalman filter
Wu, W.,
Black, M.J., Gao, Y., Bienenstock, E., Serruya, M. and Donoghue, J.P.
In
SAB’02-Workshop on Motor Control in Humans and Robots: On the Interplay of Real Brains and Artificial Devices,
pages 66-73,
Edinburgh, Scotland (UK).
August
2002.
[Share]
Sending email...

Robust parameterized component analysis: Theory and applications to 2D facial modeling
De la Torre, F. and
Black, M.J.
In
European Conf. on Computer Vision, ECCV 2002,
Springer-Verlag,
Vol. 4,
LNCS 2353,
pages 653-669,
2002.
[Share]
Sending email...


A layered motion representation with occlusion and compact spatial support
Fleet, D.J., Jepson, A. and
Black, M.J.
In
European Conf. on Computer Vision, ECCV 2002,
Springer-Verlag ,
Vol. 1,
LNCS 2353,
pages 692-706,
2002.
Abstract:
▸
We describe a 2.5D layered representation for visual motion analysis. The representation provides a global interpretation of image motion in terms of several spatially localized foreground regions along with a background region. Each of these regions comprises a parametric shape model and a parametric motion model. The representation also contains depth ordering so visibility and occlusion are rightly included in the estimation of the model parameters. Finally, because the number of objects, their positions, shapes and sizes, and their relative depths are all unknown, initial models are drawn from a proposal distribution, and then compared using a penalized likelihood criterion. This allows us to automatically initialize new models, and to compare different depth orderings.
[Share]
Sending email...